So now as we approach the final throes of PCI-DSS v3.2.1, the remaining 3 weeks is all that is left of this venerable standard before we say farewell once and for all.
PCI-DSS V4.0 is a relative youngster and we are already doing hours of updates with our customers on the things they need to prepare for. Don’t underestimate v4.0! While its not a time to panic, it’s also not a time to just lie back and think that v4.0 is not significant. It is.
Below is a table that provides an insight of the major changes we are facing in v4.0.
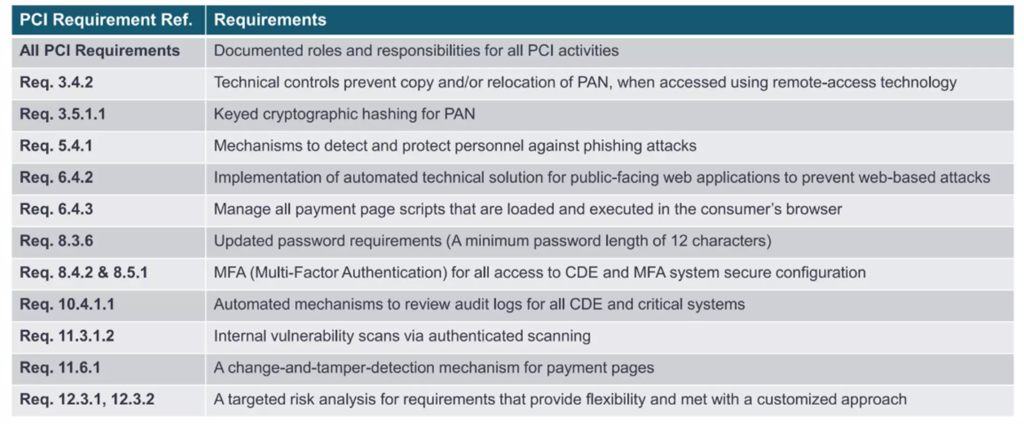
Bearing in mind that most of the requirements now start off with keeping policies updated and document roles and responsibilities, the major changes are worth a little bit of focus. In the next series of articles, we will go through each one as thoroughly as we can and try to understand the context in which it exists on.
Let’s start off the one on the top bin. Requirement 3.4.2.
Req. 3.4.2: When using remote-access technologies, technical controls prevent copy and/or relocation of PAN for all personnel, except for those with documented, explicit authorization and a legitimate, defined business need
PCI v4.0
Ok, we have underlined and emphasized a few key points in this statement. Because we feel that is important. Let’s start with what 3.4.2 applies to.
It applies to: Remote Access
It requires: Technical Controls
It must: PREVENT THE COPYING/RELOCATION
Of the subject matter: Full Primary Account Number
In v3.2.1 this was found in section 12.3.10 with slightly different wordings.
Req 12.3.10 For personnel accessing cardholder data via remote-access technologies, prohibit the copying, moving, and storage of cardholder data onto local hard drives and removable electronic media, unless explicitly authorized for a defined business need. Where there is an authorized business need, the usage policies must require the data be protected in accordance with all applicable PCI DSS Requirements.
PCI v3.2.1
I think 4.0, aside from the relocation of the requirement to the more relevant requirement 3 (as opposed to requirement 12, which we call the homeless requirement for any controls that don’t seem to fall into any other earlier requirements), reads better. Firstly, putting it in requirement 3 puts the onus on the reader to consider this as part of protection of storage of account data which is the point of Requirement 3. Furthermore, digging into the sub-requirement, 3.4 section header states: Access to displays of full PAN and ability to copy PAN is restricted.
This is the context of it, where we find the child of this 3.4 section called 3.4.2 and we need to understand it first, before we go out and start shopping for the first DLP system on the market and yell out “WE ARE COMPLIANT!”
3.4 talks about displays of FULL PAN. So we aren’t talking about truncated, or encrypted PAN here. So in theory, if you copy out a truncated PAN or encrypted PAN, you shouldn’t trigger 3.4.2. Its specific to full PAN. While we are at it, we aren’t even talking about cardholder data. A PAN is part of cardholder data, while not all cardholder data is PAN. Like the Hulk is part of the Avengers but not all Avengers are the Hulk. So if you want to copy the cardholder name or expiration date for whatever reasons like data analysis, behavioural prediction, stalking etc…this isn’t the requirement you are looking for.
Perhaps this is a good time to remind ourselves what is Account Data, Card Holder Data and Sensitive Authentication Data (SAD).
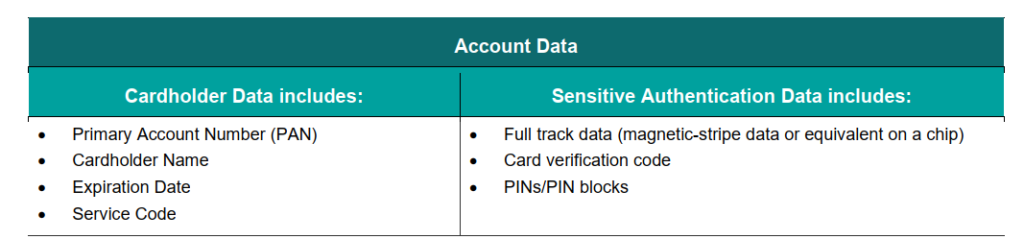
The previous v3.2.1 doesn’t actually state ‘technical controls’, which goes to say that if it’s a documentary controls, or a policy control, or something in the Acceptable Use Policy, it can also pass off as compliant. V4.0 removes that ambiguity. Of course, the policy should be there, but technical controls are specific. It has to be technical. It can’t be, oh wait, I have a nice paragraph in section 145.54(d)(i)(iii)(ab)(2.4601) in my information security acceptance document that stated this!
So these technical control(s) must PREVENT copying and relocation. Firstly just to be clear, copy is Ctrl-C and Ctrl-V somewhere else. Relocation is Ctrl-X and Ctrl-V somewhere else. Both has its problem. In copying, we will end up PAN having multiple locations of existence. In relocation, the PAN is moved, and now systems accessing the previous location will throw up an error – causing system integrity and performance issues. Suffice to say, v4.0 demands the prevention of both happening to PAN. Unless you have a need that is:
a) DOCUMENTED
b) EXPLICITLY AUTHORIZED (not Implied)
c) LEGITIMATE
d) DEFINED
When a business need is both “documented” and “defined,” it means that the requirement has been both precisely articulated (defined) and recorded in an official capacity (documented). So a list of people with access is needed for the who, why they legitimately need to access/copy/relocate PAN in terms of their business, explicitly authorized by proper authority (not themselves, obviously).
Finally, let’s talk about technical controls. Now, remember, this applies to REMOTE ACCESS. I’ve heard of clients who says, hey no worries, we have logging and monitoring in place for internal users. Or we have web application firewall in place. Or we have cloudflare in place. Or we have a thermonuclear rocket in place to release in case we get attacked. This control already implies ‘remote access’ into the environment. The users have passed the perimeter. It implies they are already trusted personnel, or contractors or service providers with properly authorized REMOTE ACCESS. Also, note that the authorization here is NOT for remote access, it is for the explicit action of copy/relocating PAN. In this case, most people would probably not have a business reason of copying/relocating PAN to their own systems unless for very specific business flow requirements. This means, only very few people in your organization should have this applied to them, under very specific circumstances. An actual real life example would be for an insurance client we have, they had to copy all transaction information, including card details in an encrypted format and put it into a removable media (like a CD-ROM) and then send it over to the Ombudsman for Financial Services as part of a regulatory requirement. That’s pretty specific.
So what passess off as a ‘technical control’? A Technical control may be as simple as to completely prevent copy/paste or cut/paste ability when accessing via remote access. This can be done in RDP or disable clipboard via SSLVPN. While I am not the most expert product specialist in remote access technologies, I can venture to say its fairly common to have these controls inbuilt into the remote access product. So, there may not be a need for DLP in that sense, as the goal here is to prevent the copying and relocation of PAN.
Now that being said, an umbrella disallow of copy and paste may not go well with some suits or C-levels who want to copy stuff to their drive to work while they are in the Bahamas. Of course. You could provide certain granular controls, depending on your VPN product or which part of the network they access. If a granular control cannot be agreed on, then a possible way is to enforce proper control via DLP (Data Loss Prevention) in endpoint protection. Or control access to CDE/PAN via a hardened jump server that has local policy locked down. So the general VPN into company resources may be more lax, but the moment access to PAN is required, 3.4.2 technical controls come in play.
At the end, how you justify your technical controls could be through a myriad of ways. The importance is of course, cost and efficiency. It has to make cost sense and it must not require your users to jump through hoops like a circus monkey.
So there you have it, a break down of 3.4.2. We are hopping into the next one in the next article so stay tuned. If you have any queries on PCI-DSS v4.0 or other related cybersecurity needs, be it SOC1 or 2, ISO27001, ISO20000, NIST or whether Apollo 11 really landed on the moon in 1969, drop us a note at avantedge@pkfmalaysia.com and we will get back to you!

Leave a Reply